Faster sites are indicative of well-maintained design and coding. They are also indicative of the condition of the database behind your CMS – something that is often overlooked because it is unseen. WordPress (WP) stores all your content in your database, including:
PagesCommentsBlog postsTheme settingsPlugin settingsPortfolio itemsForm entriesLinksWebsite settings
If you update your website regularly, the longer you have your WP site, the more data it will have and the larger the database will be. Overly large databases will affect how your site performs and take longer to retrieve the information for your users. Since WP stores everything you need in your database AND many things you don’t, cleaning up your database regularly is essential. By removing unnecessary data, you can improve the efficiency of your website.
Back Up Your Site
Before you do anything to your database, make sure you do a backup of your website. It’s always better to be safe than sorry. If something goes wrong while cleaning up your database, a complete backup can be restored to fix anything that might break during the process.
Optimize Your Tables Using phpMyAdmin
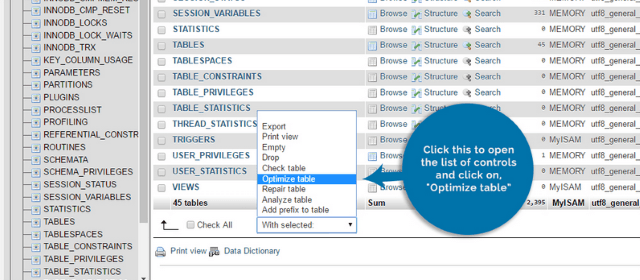
phpMyAdmin is a free web application and a common way to manage your WP database. It enables you to work with the MySQL database management system via a convenient Graphical User Interface (GUI). If your hosting provides access to cPanel, you can access your phpMyAdmin tool from your cPanel under Databases. From inside the phpMyAdmin control panel, find and click on the database that corresponds to the WP website you want to clean up. You will now be able to access all the data tables from the site you want to optimize and clean up. If you have several databases and don’t know which one is the correct one, access your wp-config.php file by logging into your cPanel and locating your file manager. Look inside the root folder for the website you want to clean up. Find the wp-config.php file, right-click on it and then select edit. Look for DB_NAME to identify the name of the database for the site you are working on. Once you have determined the name of the database, close File Manager and cPanel. Log back into phpMyAdmin. Scroll to the bottom of the table list and look for and click select all. You will see that it says With selected. Click on Optimize table. phpMyAdmin will then run a defragmenting application automatically.
Delete Unused Plugins & Themes
Plugins and themes take up a lot of space in your database. Removing any you aren’t using is an easy way to reduce the size of your database. To search your installed plugins, log into your WP dashboard, hover over Plugins and click Installed Plugins. WP users often test many themes before they choose the design to use. Did you remove the themes you aren’t using? To check, go to your WP dashboard and click on Appearance–>Themes to see if there is more than one. Even deactivated themes are still taking up room in your database. This is not the case. You must make sure to delete it completely.
Delete Old Outdated Posts
If there is one thing you can be sure of regarding the Internet is that things change – constantly. So if you have been running a blog for many years, it is highly possible that many of your older posts are no longer relevant or accurate. Do not just start deleting outdated content. You should first do a content audit and make sure you redirect the URLs of that content before you delete it. You do not want to be eliminating any incoming links you may have. You will also want to make sure anyone coming to your site through that link is taken to a related post not a “404 page not found” message.
Keep Your Site Updated
Old versions of WordPress, themes and plugins can wreak havoc on your website and its corresponding database. Problems range from compatibility issues to security holes that can slow down or even break your site. Some WP designers like to wait for a short time when a newer version of WordPress comes out so that all the kinks are worked out. Let other people find the bugs so you don’t have to do it. Make it a habit to update WordPress, your theme, and all your plugins soon after a new version is released.
Use WordPress Plugins
As with most WP needs, there’s a plugin for that. WordPress offers many database cleaning plugins to help you keep your site clean and uncluttered. Below are some of the more popular and helpful ones. When choosing a plugin, you want to make sure it is compatible with your version of WP, is still maintained, and has been updated recently.
WP-Optimize
One of the most powerful and effective plugins to clean your database and boost your WP performance is WP-Optimize. It is easy-to-use and mobile-friendly. Some of its features include:
Defragmenting the MYSQL tables.Optimizing your database without having to run queries manually.Removing unnecessary data like spam comments, pingbacks, and trackbacks.
WP Clean Up Optimizer
If you want to optimize your WordPress site and also clean up unnecessary data from your database without having to use phpMyAdmin, WP Clean Up Optimizer is the plugin for you. Some of the things cleaned up by this plugin include:
Revisions.Deleted posts.Comments in pending, spam, or trash.Auto drafts.Pingbacks and trackbacks.Duplicated comment meta.Unused terms.Duplicated post meta.
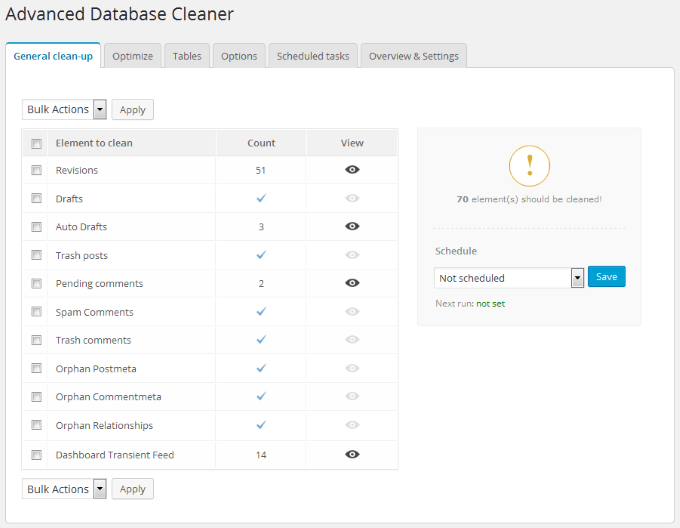
Advanced Database Cleaner
When you delete old pages or post revisions from your WP dashboard, it leaves some unnecessary files in your database. These files slow down your site. Advanced Database Cleaner will find those files, also called orphaned items to reduce your database size and improve your site speed. Some of the orphans it deletes are:
Comments in trash, spam, or pending.Old revisions of posts and pages.Orphan post meta.Old auto drafts.
You can also schedule your database to optimize and run automatically. Optimizing and cleaning up your WordPress database contributes to the overall performance and speed of your website.This will lead to a better user experience and more traffic from search engines. As outlined above, there are several things you can do to organize and declutter your database. For the less technical WordPress users, it is easier to use WP plugins than to work with phpMyAdmin.