These tips will help you to reduce the strain Chrome takes on your CPU and minimize the memory (RAM) the browser uses. Hopefully following these tips will help performance regardless of whether Chrome is in the foreground or running in the background. We’ll start by looking at Google’s suggested optimization tips and then we’ll share some lesser known tools after.
Steps for Optimizing Google Chrome
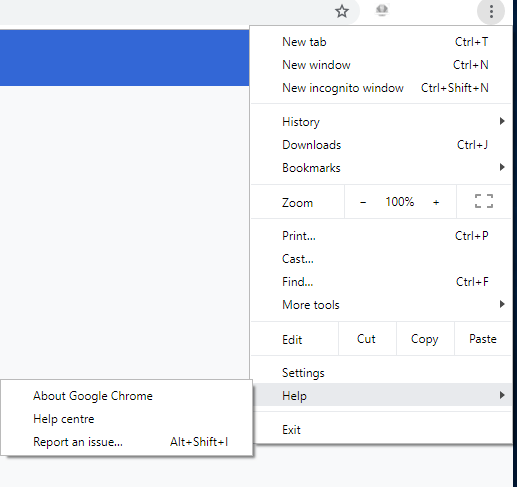
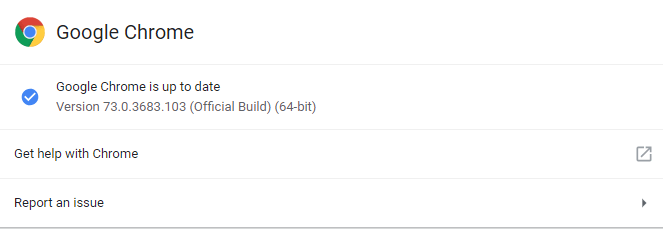
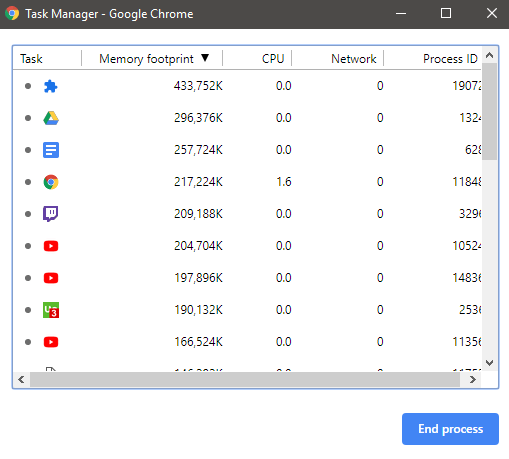
Our first suggestion would be to install the latest Google Chrome updates. This could include new optimizations and fixes for potential incompatibilities with your current hardware. To update Google Chrome, click the three dots in the top right. At the bottom, hover over ‘help’ and then click ‘About Google Chrome’. This will take you to a page where you can see if you need to update Chrome. If there is an update available, you’ll be notified here and you’ll be able to update Chrome. Once you’ve checked to see whether Chrome has been updated, you can now move to Chrome’s built-in task manager. This menu is something most people are unaware of and it can help you to reduce Chrome’s memory and CPU usage. To access the task manager, click the three dots in the top right. Hover over ‘more tools’ and then select ‘task manager’. In Task Manager, you’ll be able to see which apps and tabs use the most memory and CPU power within Chrome. You may be surprised at some of the usage here. For example, I had the Google Drive tab in the background and it was using 430MB of RAM and I wasn’t even using it. You can close down apps and tabs here or close task manager and then end them manually.
General Chrome Maintenance Tips
On top of these two tips, being more aware of how many tabs you have open at once can help Chrome to be less resource intensive. Each tab has its own impact on your performance, so 10 or more tabs will only increase the strain on your PC tenfold. If you want to reduce the strain further, you could take apps you use outside of Chrome by downloading standalone software. For example, picking up Word, WordPad, or even the desktop version of Google Drive instead of using Chrome. You could also use Spotify instead of YouTube for music. Consider using standalone apps for everything so that Chrome isn’t such a memory hog, and remember to close those apps when you aren’t using them.
Remove Extensions or Viruses
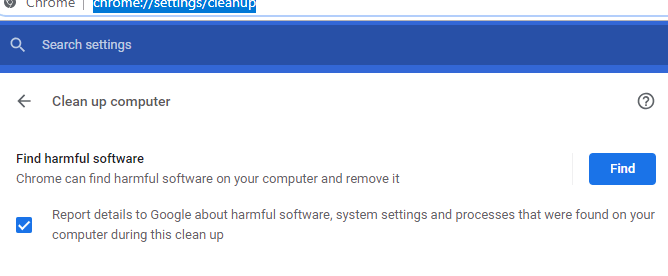
You can find potentially harmful apps or extensions installed on your Chrome browser by visiting chrome://settings/cleanup. In some cases, malicious extensions may have been installed on your PC and this page shown above will remove them for you. Malicious extensions may make adverts pop up or make other processes run in the background that can increase the strain Chrome has on your PC. Sometimes non-malicious extensions can have a big impact on your Chrome’s performance too. To check through your extensions and remove those you don’t need, visit chrome://extensions/ and consider deleting the ones you don’t need. You may find that there are extensions installed that you never even use and these could be running in the background. If you’re not sure what impact a particular extension may have on your performance, you can refer to the task manager we mentioned earlier. Extensions will appear there, too. You’ll need to delete them from the extensions page, however.
Use Extensions to Manage Performance
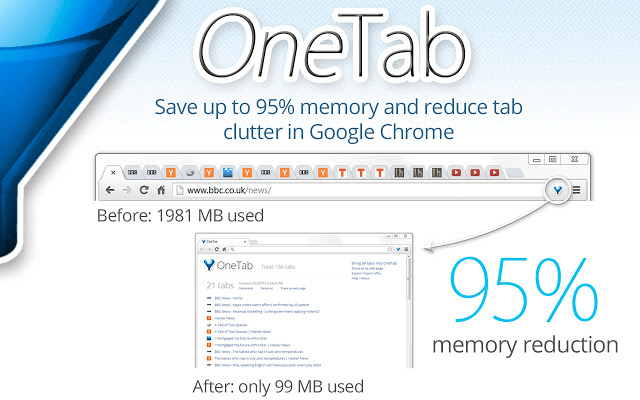
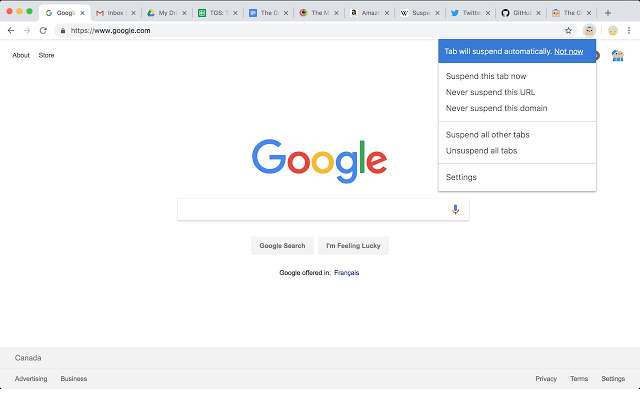
After removing unneeded extensions, it may seem counterintuitive to go and install more, but there are some extensions that can improve performance. We’ve picked out three below that people may be unaware of. All of these are designed to help monitor and reduce the strain Chrome has on your PC. OneTab OneTab is a Chrome extension that can move all of your open tabs into a single list. You can then use the list to re-open or close tabs at any point. The list won’t take much of an impact on your performance and it is far better than having all of those tabs open and running in the background. Tab Wrangler Tab Wrangler is another option, specifically aimed at those that forget to close all of their tabs. It will close tabs automatically after they are left idle for a designated time. You can also set certain apps, tabs or websites to never close and set up more rules so that everything is automated. Eventually, all you have to worry about is browsing and Tab Wrangler will do the rest for you. The Great Suspender The Great Suspender is similar to Tab Wrangler, but instead of closing tabs, The Great Suspender will simply suspend tabs you aren’t using. This means that you can browse with lots of tabs open without impacting performance. When you switch tabs, those tabs will start running like normal again. There are settings available to whitelist certain websites or stop pinned tabs from being suspended, so you have a lot of control over how the extension works.
Summary
That wraps up our guide on how to make Chrome less resource intensive. We hope that this guide has been useful. If you need some more tips or advice, leave a comment and I’ll try to help when I can.